Gastroparesis Affects 12 To 15% Of People Living With Diabetes
What is gastroparesis?
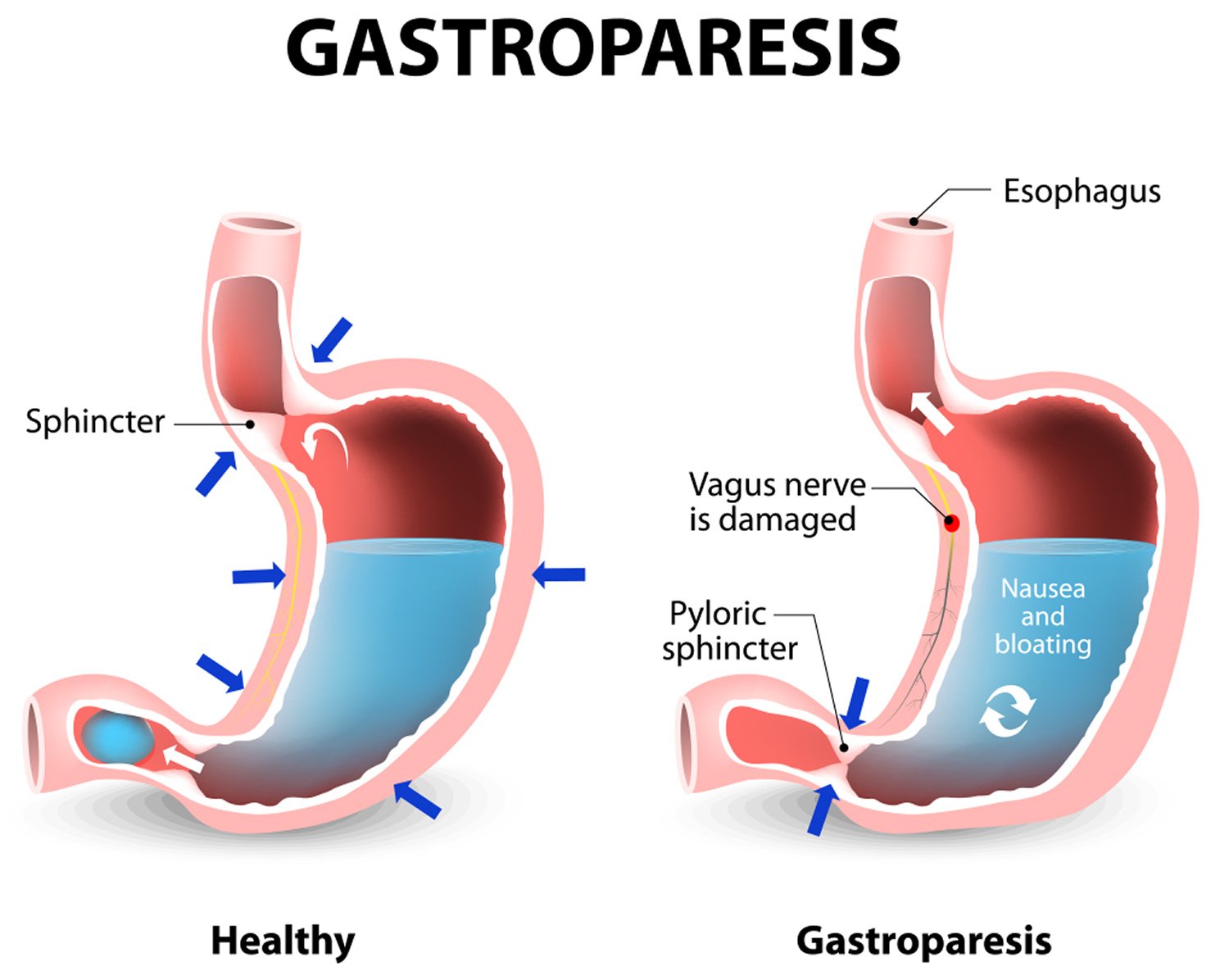
Gastroparesis is a condition when the stomach takes a long time to empty its contents into the small intestine. It is also referred to as delayed gastric emptying, gastric stasis, slow stomach, lazy stomach, and diabetic enteropathy. It usually occurs in people who have been living with diabetes for at least 10 years, and typically presents together with complications of the eye, kidney and others linked to the nervous system.
Normally, when food is swallowed, the muscles in the stomach wall help break the food down into smaller pieces, pushing it into the small intestine to continue digestion. This action is controlled by the vagus nerve, part of the so-called autonomic nervous system, which automatically regulates many bodily functions such as breathing and heart rhythm. If the vagus nerve is damaged or stops working, the muscles in the stomach and intestines do not function normally, and the movement of food stops or slows down. If the food stays in the stomach too long, the food ferments and causes an overgrowth of gas-producing bacteria.
Management And Treatment Of The Disease
Diabetic Gastroparesis/Gastropathy
Management of gastroparesis requires optimization of glycemic control both acute and chronically. Blood glucose levels > 270 mg/dL prolongs gastric emptying time.
Dietary Recommendations: Vitamin and mineral deficiencies may be seen in patient with gastroparesis due to food intolerance. Diet modifications are needed to compensate for impaired gastric motor and sensory function. The gastroparesis diet requires 4-6 small, low fat, low fiber meals each day . Patients may be dependent on high calorie liquids to meet their caloric and nutritional needs during flares when they are unable to tolerate solid food. Carbonated beverages and alcohol should be avoided. In severe cases, patients may need a jejunal feeding tube to bypass the stomach.
Medication Therapy: Medications used for diabetic gastroparesis include prokinetic drugs that stimulate gastric emptying and symptomatic treatment with antiemetic agents, and neuromodulators that blunt gastric nerve hypersensitivity.
Prokinetic Therapy
Erythromycin is a motilin agonist that is most effective when used intravenously at 3 mg/kg every 8 hours. While it may be given in oral formulation, studies have shown that long term use leads to downregulation of the motilin receptor, and as a result, the medication becomes ineffective. Drug interactions with CYP3A4 activity and QT prolongation may occur.
Symptomatic Management
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Diabetic Constipation
Table V.
Table VI.
Managing Diabetes Differently With Gastroparesis
The trickiest part of managing your blood sugars with gastroparesis is that youre never quite sure when the food you ate is going to be fully digested and make its way into your bloodstream, eventually raising your blood sugar.
Youll find that some mealsor entire daysdigest normally while other days the food you eat will digest unpredictably slowly, impacting your blood sugar in a way that feels nearly impossible to accurately time your insulin doses around.
One of the most helpful tools for learning when to safely administer insulin for your meals is going to be a continuous glucose monitor . A diagnosis of diabetic gastroparesis should absolutely qualify you for health insurance coverage, just make sure your doctor emphasizes this diagnosis in the paperwork.
You May Like: How To Flatten Stomach Exercises
Key Laboratory And Imaging Tests
Diabetic Gastroparesis/Gastropathy
Diagnosis of gastroparesis requires objective evidence of delayed gastric emptying. Patients should be evaluated for complications of vomiting and alternative causes of delayed gastric emptying, such as mechanical obstruction.
Laboratory Studies: A basic metabolic panel is needed to identify electrolyte abnormalities and evidence of dehydration, particularly hypokalemia, contraction alkalosis and elevated blood urea nitrogen or creatinine levels. Complete blood count and thyroid-stimulating hormone are typically checked to rule out alternative etiologies.
Structural Evaluation: Upper endoscopy is needed to rule out gastric outlet obstruction secondary to stricture, ulcer disease, or neoplasm. Retained food or bezoars may be found on endoscopic evaluation. A plain upright abdominal radiograph, upper gastrointestinal contrast radiography, or computed tomography can be obtained if more distal obstruction is suspected. If abdominal pain is a prominent symptom or liver chemistries are abnormal, then abdominal ultrasound may be considered to exclude a hepatobiliary cause such as symptomatic gallstone disease.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Laboratory tests are most useful for assessing nutritional and metabolic consequences but cannot diagnose SIBO.
Diabetic Constipation
Diagnostic testing may not be necessary in patients with diabetic constipation unless presentation suggests the need to exclude other potential causes of symptoms.
What Is Diabetic Ketoacidosis

Diabetic ketoacidosis happens when your blood sugar is high and your insulin level is low. This imbalance in the body causes a build-up of ketones. Ketones are toxic. If DKA isnt treated, it can lead to diabetic coma and even death.
DKA mainly affects people who have type 1 diabetes. But it can also happen with other types of diabetes, including type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes .
Don’t Miss: How To Help Heal Stomach Ulcers
Complications Of Diabetic Gastroparesis
When your body isnt able to properly digest food, a variety of complications can developeven before youve been properly diagnosed with gastroparesis.
- Dehydration due to frequent vomiting
- Malnutrition due to poor absorption of nutrients in the food you eat
- Difficulty managing your blood sugar levels after eating
- Low-calorie intake or difficulty getting enough calories
- Bezoars
- Difficulty maintaining a healthy weight due to inability to eat enough
- Overall lower quality of life due to malnutrition and pain
Lauras Story My First Symptoms
My first symptoms started six years prior to my diagnosis, Laura Marie told Diabetes Strong. Laura has lived with type 1 diabetes since 2002, when she was 16 years old. Her diabetic gastroparesis diagnosis was in 2014.
My symptoms of gastroparesis included nausea and vomiting, often feeling nauseous in the mornings and vomiting undigested food hours or ever even days after Id eaten it.
Laura says she had gradually become incredibly bloated. The bloating was severe enough that her clothing felt remarkably uncomfortable by the end of each day. And on top of bloating, she had started experiencing severe cramping and pain in her stomach.
My blood sugar levels also proved to be very erraticI would have a low blood sugar after eating, and a high blood sugar hours later, especially throughout the night.
By eventually wearing a Continuous Glucose Monitor , Laura says she could see the full evidence of her erratic overnight blood sugars.
The scariest part of her symptoms, though, was the increasingly frequent visits to the Emergency Room for DKA . Laura says she was usually admitted to the hospital about every 6 months because her unmanageable blood sugars would lead to DKA.
It was after being in DKA for what seemed like the hundredth time that I became so burnt-out, frustrated, and scared, that I told my healthcare professionals I was desperate for tests and a diagnosis.
Also Check: Why Do I Have Stomach Acid
What Happens To A Diabetic Who Is Not Receiving Insulin
Without insulin, your body will begin to break down its own fat and muscle, which will result in weight loss. This can result in a life-threatening disease known as diabetic ketoacidosis. This occurs when the bloodstream becomes acidic, toxic levels of ketones accumulate in the bloodstream, and severe dehydration occurs.
Can Diabetes Cause Left Abdominal Pain
What effect does diabetes have on the abdomen? Normally, your stomach muscles contract to aid in the passage of food through the digestive tract. Nerve damage from high blood sugar can induce gastroparesis, causing those muscles to slow down or stop working altogether. Your stomach isnt emptying properly, so your food may take a long time to leave.
Is it possible for diabetes to induce pain in the left flank? In a diabetic patient with a fever and flank pain, emphysematous pyelonephritis should be suspected . If EPN is not diagnosed and treated early, the clinical course can be severe and life-threatening.
Is it possible for type 2 diabetes to produce stomach pain? Lower gastrointestinal symptoms, such as constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, bloating, intestinal gas, and floating stools, were shown to be substantially more common in the study participants.
This groundbreaking technique has helped thousands of individuals with unpredictable blood sugar levels
To assist them in burning toxic fat from their essential organs and stomachs
While also naturally and successfully balancing their blood sugar levels.
Starting now
Recommended Reading: How To Lose Weight In My Stomach
Is Type 2 Diabetes A Disease That Worsens With Age
Type 2 diabetes medications Type 2 diabetes is a progressive disease that typically worsens over time. Making lifestyle adjustments, such as changing your food and increasing your physical activity, may initially help you regulate your blood glucose levels, but may not be sufficient in the long run.
Symptoms Of Diabetic Gastroparesis
- Impaired oral drug absorption
- Spasms and cramping of the stomach wall
Its really important to discuss any distinct stomach or digestion issues with your healthcare team, says Susan Weiner, MS, RDN, CDE, CDN, FAADE and 2015 AADE Diabetes Educator of the Year. This may include chronic constipation, bloating, and recent spikes in your blood sugar levels that you dont understand or cant explain with the usual everyday challenges of diabetes management.
Weiner notes that she would hope any healthcare professional would create an open and non-judgmental environment for their patients because this can be a very uncomfortable situation for people with diabetes. Struggling with blood sugar management comes with its own inevitable layer of guilt and frustration, which means you need a healthcare team that can support you properly through a potential gastroparesis diagnosis.
Read Also: How To Get Rid Of Stomach Worms
Is Diabetes Causing You To Fart
Of course, the diabetic complication gastroparesis may be a significant fart producer, since gastroparesis essentially wrecks the digestive system. Additionally, elevated blood glucose levels might result in greater farting in certain individuals due to the extra sugar fueling an overgrowth of normal gut flora.
I was just diagnosed with high blood sugar for the first time in my life. Im 48 years old. Diabetes runs in my family. I had no idea Id acquire it, but my doctor stated it was at an all-time high of 275+ and that I needed medication. I turned down the doctors offer and asked for a month to get it under control and rechecked. I got the pills here and began using them in conjunction with my diet. My doctor gave me the tester so I could monitor my blood level at home. After a week of taking it once in the morning before breakfast and once in the afternoon before lunch. Id check it in the evening. Surprisingly, it was at 102,105, and once at 98. And depending on what and how much I eat, it would rise to 120-128 after supper. A month later, I returned for my checkup, and everything was OK. Doctors say that if I stick to my healthy diet and exercise routine, Ill be OK. It actually works!! Ill be getting another bottle shortly.
What Is The Outcome If Diabetic Ketoacidosis Is Left Untreated
Increased levels of ketones in the bloodstream impair the proper functioning of several organs and systems throughout the body. The higher the level of ketones in the blood, the more unwell a person suffering from diabetic ketoacidosis becomes. Diabetes ketoacidosis, if left untreated, may result in potentially deadly consequences such as extreme dehydration, unconsciousness, and brain edema.
You May Like: Can Advil Help Stomach Pain
Gut Check: How To Prevent Or Control Digestive Issues In Diabetes
But just because you have diabetes doesnt mean you have to resign yourself to digestive problems as well. To help keep your digestive system in working order, follow these tips:
Keep your blood sugar tightly controlled. Whether youre looking to prevent or control digestive problems when you have diabetes, it is most important to rigorously pay attention to control blood sugar and keep your A1C within a healthy range, Reynolds says. A1C elevation is directly proportional to the level at which esophageal function and gastric function is impaired, he says. Everyones A1C goal is different talk to your doctor to learn yours.
Choose a healthy diet low in sugar and refined carbs. A diet high in refined sugar can mess up the gut bacteria, Cline says. He recommends staying away from foods high in saturated fat and refined carbohydrates, such as white bread, pasta, and rice, as well as processed sweets and snacks, like refined pastries and granola bars.
Research also suggests eating a healthy diet could help minimize disease progression, which is associated with neuropathy. A study published in April 2017 in the journal Nature, for instance, found that a certain substance produced by gut microbes is associated with a reduced likelihood of progression of type 2 diabetes in overweight people with prediabetes. That substance, indolepropionic acid, is linked with dietary fiber intake, the authors noted.
How Diabetic Neuropathy Can Lead To Heartburn And Other Issues
So how might diabetes affect the digestive system? Advanced diabetes, whether its from type 1 or type 2 diabetes, can affect any organ in the body including those organs in the digestive tract, says James C. Reynolds, MD, a gastroenterology specialist and clinical medicine professor at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia.
Dr. Reynolds notes digestive problems may be caused by the very factors that led to diabetes in the first place, such as obesity, but its also possible that digestive problems are the result of diabetes-related complications, such as hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar.
One of the most serious diabetes complications that can result from consistent high blood sugar is diabetic neuropathy, or nerve damage. Neuropathy may lead to weakness, pain, and numbness, affecting feeling in your feet, legs, and hands, but the condition can also affect digestive functions like swallowing and constipation, Reynolds explains.
If you have diabetes, this potential complication is just another reason its crucial to pay attention to your A1C, the average level of glucose over the past two to three months, Reynolds says.
Read Also: Why Am I Gaining Weight In My Lower Stomach
Does Metformin Cause Diarrhea
Many people with type 2 diabetes use the medication metformin to help control their blood sugar. Diarrhea is a common side effect when a person first begins taking metformin. Occasionally, people will experience chronic diarrhea after theyve been on the medication for a long time, even years.
If you are a type 2 diabetic on metformin who is experiencing chronic diarrhea, talk to your healthcare provider about whether there are other options available to help control your blood sugar.
Why Do Diabetics Perspire Throughout The Night
Night sweats are often induced by hypoglycemia, which may occur in persons who use insulin or the diabetic drug sulfonylureas. When your blood glucose levels go dangerously low, you release an excessive amount of adrenaline, which results in perspiration. Sweating should cease as your blood glucose returns to normal.
You May Like: How To Get Rid Of Crepey Skin On Stomach
Is Diabetes A Possible Cause Of Excessive Gas
Of course, the diabetes complication gastroparesis can be a significant fart generator, as gastroparesis essentially wrecks the digestive system. Additionally, elevated blood glucose levels might result in greater farting in some individuals due to the excess sugar fueling an overgrowth of normal gut bacteria.
Other Tests That May Prove Helpful Diagnostically
The previous section detailed the diagnostic evaluations that typically may be performed to assess each of the potential GI complications of diabetes. The following text discusses additional testing that may be considered for patients unresponsive to appropriate therapy or for whom alternate rare diagnoses are possibilities.
Diabetic Gastroparesis/Gastropathy
Antroduodenal manometry uses a catheter to record phasic contractions in the antrum and proximal small bowel. Normal recordings show normal migrating motor complex activity, an organized pattern that clears the upper gut of undigested debris, and a contractile response to meals or motor stimulating medications. Abnormalities that may be detected include pylorospasm , visceral neuropathy , visceral myopathy , and rumination .
Electrogastrography is rarely performed to assess for abnormal cycling of the gastric electrical pacemaker that controls normal propagation of contractions in the distal stomach. This involves placing electrodes on the skin overlying the stomach and recording activity during fasting and after a meal. Normal EGG tracings show uniform electrical oscillations with a frequency of 3 cycles per minute that increase in amplitude with eating. Patients with gastroparesis may have cycling that is too fast or too slow or waveforms that do not increase in amplitude after a meal.
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth
Diabetic Constipation
Diabetic Diarrhea
Miscellaneous GI Complications of Diabetes
You May Like: What To Use For Bloated Stomach
Dietary Management Is Key To Improving Gi Symptoms
For some individuals the easiest method for feeling bettera semi-liquid dietcan be hard to implement, says Dr. Grover. The way to reduce most of the unpleasant symptoms is to blend up solid food into a soft paste, which solves the problem of poor gastric emptying, but this is often unappealing and so not readily embraced.
Dr. Camilleri agrees liquids and blended solid foods are often much better tolerated but his patients find it distasteful. So hell often say, Consider this: blending up a peanut butter sandwich is a better option than tube feeding, which may happen if the symptoms get bad and last long enough. Often, individuals who are very rigorous with their diet are able to avoid the need for medications altogether,6 the doctors point out.
Many patientsabout 80%can avoid tube feeding by adjusting your diet to facilitate speedy gastric emptying.6 Dr. Camilleri says: Gastroparesis is a chronic condition that will probably not go away but also isn’t likely to get worse.
Be aware of the potential for nutrient deficiencies of some minerals, like copper and zinc,6 says Dr. Grover. This is more likely to occur when the condition has been present a long time. He also warns against any suggestion that you are a candidate for gastric bypass surgery or removing the stomach as a way to manage the symptoms. This often replaces one problem with another, he says.
Neither doctor has any financial conflicts regarding this discussion.