How Does My Doctor Know I Have Stomach Cancer
Q: What do I do if I think I have stomach cancer?A: If there is any reason to suspect stomach cancer, your doctor will ask you questions about risk factors and symptoms and do a complete physical exam. The doctor will feel your abdomen to see if there are any abnormal changes. You may need to have some tests done to find out what’s going on.
Tests that may be done to find stomach cancer
Q: How is stomach cancer diagnosed?A: Doctors often divide stomach cancers into 2 groups. Resectable cancers are those the doctor thinks can be completely removed during surgery. Unresectable cancers are those that can’t be completely removed. This might be because the tumor has grown into nearby structures or lymph nodes. Or it may have grown too close to major blood vessels, or has spread to distant parts of the body.
Q: What is the staging of stomach cancer?A: Staging is the process of finding out how far the cancer has spread. This is very important because the treatment and the outlook for your recovery depend on the stage of the cancer. After stage 0 , stages are labeled using Roman numerals I through IV . As a rule, the lower the number, the less the cancer has spread. A higher number, such as stage IV , means a more serious cancer.
After looking at your test results, the doctor will tell you the stage of your cancer. Be sure to ask your doctor to explain your stage in a way you understand. This will help you both decide on the best treatment for you.
- Endoscopic mucosal resection
When Should You Check Your Poo
As a general rule of thumb, you should look at your poo every time you go to the toilet.
Checking your stool regularly is the only way to know what is normal for you, and be able to identify a change in the colour, consistency or frequency of your toilet habits.
Keeping a diary of changes can also be helpful to your doctor if you are concerned about any visible changes to the colour, shape or texture.
Regular NHS bowel cancer screening is also rolled out by the NHS to reduce the risk of people dying from bowel cancer, though this is currently only available to people aged 60 to 74-years-old.
The NHS said: The programme is expanding to make it available to everyone aged 50 to 59 years. This is happening gradually over four years and started in April 2021.
You use a home test kit, called a faecal immunochemical test , to collect a small sample of poo and send it to a lab. This is checked for tiny amounts of blood.
Even if you dont have symptoms, you should still speak to a GP for advice if you have a family history of bowel cancer.
Hereditary Causes Of Stomach Cancer
Inheriting certain genetic diseases puts you at risk of getting stomach cancer and being diagnosed earlier in life. Inherited conditions that influence your risk include:
- Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer is rare, but when it is found the risk of developing stomach cancer is between 70 and 80 percent. A problem with a gene called CDH1 causes this type of stomach cancer, and in women it is associated with a higher risk of breast cancer.
- Lynch syndrome, also called hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer, is a condition that also increases the risk of stomach cancer. Problems with genes called MLH1 or MSH2 and several others lead to Lynch syndrome.
- Familial adenomatous polyposis involves developing multiple noncancerous polyps in the colon, stomach and intestines that may later progress to cancer. This condition, caused by a defect in the APC gene, most often leads to colorectal cancer but in some cases it increases risk for stomach cancer.
- BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are more commonly associated with breast cancer, but may also increase the risk of stomach cancer.
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome increases the risk of developing stomach cancer at a young age.
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome leads to polyps in several passages in the body, including the nose, lungs, bladder, stomach and intestines, and is associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer.
Don’t Miss: What Causes Stomach Pain Every Time You Eat
Medical History Physical Exam And Tests To Look For Bleeding
When taking your medical history, the doctor will ask about your symptoms and possible risk factors to see if they might suggest stomach cancer or another cause. The physical examcan give your doctor information about possible signs of stomach cancer or other health problems. In particular, the doctor will feel your belly for anything abnormal.
The doctor might order a blood test to look for anemia , which could be caused by the cancer bleeding into the stomach. A test might also be done to look for blood in your stool that can’t be seen by the naked eye, which could also be a sign of bleeding in the stomach.
If your doctor thinks you might have stomach cancer or another type of stomach problem, he or she will likely refer you to a gastroenterologist , who will examine you and might do further testing.
Diagnosis Of Stomach Cancer

Diagnosing stomach cancer usually begins with a visit to your family doctor. Your doctor will ask you about any symptoms you have and do a physical exam. Based on this information, your doctor may refer you to a specialist or order tests to check for stomach cancer or other health problems.
The process of diagnosis may seem long and frustrating. Its normal to worry, but try to remember that other health conditions can cause similar symptoms as stomach cancer. Its important for the healthcare team to rule out other reasons for a health problem before making a diagnosis of stomach cancer.
The following tests are commonly used to rule out or diagnose stomach cancer. Many of the same tests used to diagnose cancer are used to find out the stage, which is how far the cancer has progressed. Your doctor may also order other tests to check your general health and to help plan your treatment.
Don’t Miss: What To Take For Stomach Bug
Why You Might Have A Gastroscopy
You might have a gastroscopy to find out the cause of symptoms such as:
- abnormal bleeding
- low levels of iron
- difficulty swallowing
If you have Barrett’s oesophagus you’ll have regular gastroscopies to check for any changes to cells in the lining of your food pipe.
During the test your endoscopist takes samples of any abnormal looking areas. They send the samples to the laboratory to be looked at under a microscope.
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Stomach Cancer
The outlook for stomach cancer depends on the stage of the cancer. People in the early stages of stomach cancer have a much greater rate of survival than those at a later stage:
- If stomach cancer is found in its earliest stage and can be removed with an endoscope, the five-year survival rate is higher than 90 percent.
- If the cancer is found after it has spread to areas surrounding the stomach, the five-year survival rate is 28 percent.
- If the cancer has spread to areas beyond those surrounding the stomach, the five-year survival rate is 4 percent.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 02/17/2019.
References
You May Like: Why Is My Stomach Hurting So Much
Having Another Type Of Cancer
Your risk of developing stomach cancer is increased if you’ve had another type of cancer, such as cancer of the oesophagus or non-Hodgkin lymphoma .
For men, the risk of getting stomach cancer is increased after having prostate cancer, bladder cancer, breast cancer or testicular cancer. For women, the risk of developing stomach cancer increases after having ovarian cancer, breast cancer or cervical cancer.
Testing For Other Conditions And Cancers
Individuals who have hereditary diffuse gastric cancer syndrome and Lynch syndrome have a drastically increased risk of stomach cancer. Recognizing these and taking precautions after receiving a doctors advice can reduce the risk.
People with close family members who have had stomach cancer and those who had invasive lobular breast cancer before the age of 50 years might benefit from genetic testing.
If a test shows changes in the CDH1 gene, a doctor may recommend removing the stomach before cancer develops.
Current research is looking into the possible cancer links of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection in the stomach lining.
Early studies suggest that treating H. pylori infection with antibiotics can reduce the risk of stomach cancer, although further research is necessary.
Recommended Reading: Should Collagen Be Taken On An Empty Stomach
How Is Stomach Cancer Treated
There are several approaches to treating stomach cancer. In many cases, surgery can be avoided.
In the early stages when the cancer is limited to the superficial layers of the stomach, the cancer can be removed through an upper endoscopy performed by a gastroenterologist. In this procedure , the tumor is dissected from the rest of the gastric wall and removed through the mouth.
Once the tumor invades beyond the superficial layers of the stomach, surgery will be required to remove the stomach and connect the esophagus to the small intestines to allow for digestion.
Radiation therapy uses high-powered beams of energy to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy uses chemicals to kill the cancer cells. These treatments are generally combined.
There are also several drugs to treat stomach cancer. Treatment depends on how severe the cancer is and is decided upon by a doctor after diagnosis.
Total Gastrectomy Or Oesophagogastrectomy
If your cancer is in the middle or at the top of your stomach, you may need to have a total gastrectomy. If the cancer is close to the end of your oesophagus, where it meets your stomach, you may need to have an oesophagogastrectomy.
If you have a total gastrectomy, the end of your gullet will be joined to the top of your jejunum . If you have an oesophagogastrectomy, the remaining part of your gullet will be joined to your jejunum.
Recommended Reading: What Causes Stomach Pain And Nausea
How Can I Prevent Stomach Cancer
Treat stomach infections. If you have ulcers from an H. pylori infection, get treatment. Antibiotics can kill the bacteria, and other drugs will heal the sores in the lining of your stomach to cut your risk of cancer.
Eat healthy. Get more fresh fruits and vegetables on your plate every day. Theyâre high in fiber and in some vitamins that can lower your cancer risk. Avoid very salty, pickled, cured, or smoked foods like hot dogs, processed lunch meats, or smoked cheeses. Keep your weight at a healthy level, too. Being overweight or obese can also raise your risk of the disease.
Donât smoke. Your stomach cancer risk doubles if you use tobacco.
Watch aspirin or NSAID use. If you take daily aspirin to prevent heart problems or NSAID drugs for arthritis, talk to your doctor about how these drugs might affect your stomach.
Show Sources
American Cancer Society: “Can Stomach Cancer Be Found Early,” “Treatment Choices by Type and Stage of Stomach Cancer,” “Chemotherapy for Stomach Cancer,” “Radiation Therapy for Stomach Cancer,” “Targeted Therapies for Stomach Cancer.”
Mayo Clinic: “Stomach Cancer.”
What Are The Different Types Of Stomach Cancer
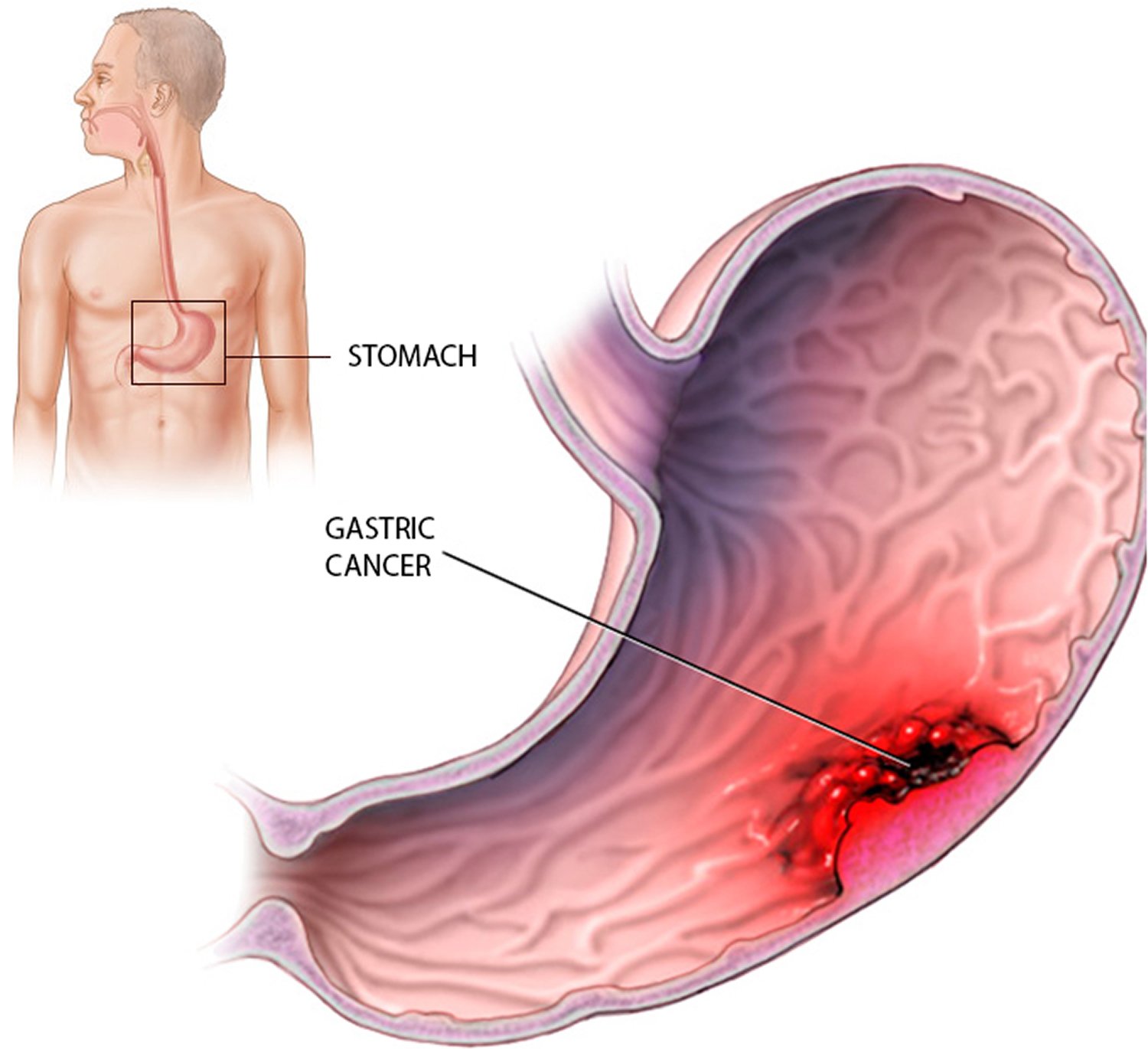
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is the name for a category of cancer. There are many different types of stomach cancer:
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of gastric cancer, comprising more than 90% of all stomach cancers. Carcinoma that occurs in the innermost lining of the stomach.
- Lymphoma: Cancer of the immune system that accounts for 4% of all stomach cancer, which is not from the mucosa of the stomach lining. It is broken up into primary and secondary lymphoma of the stomach.
- Primary lymphoma involves the stomach and can eventually affect the lymph nodes, bone marrow and other parts of the body.
- Secondary lymphoma initially involves other parts of the body, like circulating blood, lymph nodes, bone marrow and other organs. Secondarily, cancer spreads to the stomach.
Read Also: How To Stop Your Stomach From Hurting On Your Period
Stomach Cancer Screening Patient Version
On This Page
Screening is looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. This can help find cancer at an early stage. When abnormaltissue or cancer is found early, it may be easier to treat. By the time symptoms appear, cancer may have begun to spread.
Scientists are trying to better understand which people are more likely to get certain types of cancer. They also study the things we do and the things around us to see if they cause cancer. This information helps doctors recommend who should be screened for cancer, which screening tests should be used, and how often the tests should be done.
It is important to remember that your doctor does not necessarily think you have cancer if he or she suggests a screening test. Screening tests are given when you have no cancer symptoms.
If a screening test result is abnormal, you may need to have more tests done to find out if you have cancer. These are called diagnostic tests.
Signs And Symptoms Of Stomach Cancer
Early-stage stomach cancer rarely causes symptoms. In countries where screening for stomach cancer is not routine, such as the United States, most stomach cancers arent found until theyve grown fairly large or have spread outside the stomach.
When stomach cancer does cause signs and symptoms, they can include:
- Poor appetite
- Vague discomfort in the abdomen, usually above the navel
- Feeling full after eating only a small meal
- Heartburn or indigestion
- Vomiting, with or without blood
- Swelling or fluid build-up in the abdomen
- Blood in the stool
- Feeling tired or weak, as a result of having too few red blood cells
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes , if the cancer spreads to the liver
Most of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by things other than stomach cancer, such as a viral infection or an ulcer. Some of these symptoms may also be caused by other types of cancer. But people who have any of these problems, especially if they dont go away or get worse, should see a doctor so the cause can be found and treated, if needed.
Our team is made up of doctors and oncology certified nurses with deep knowledge of cancer care as well as journalists, editors, and translators with extensive experience in medical writing.
Ku GY, Ilson DH. Chapter 72: Cancer of the Stomach. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Doroshow JH, Kastan MB, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloffs Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Elsevier 2020.
Also Check: What Are The Symptoms Of Esophageal And Stomach Cancer
Early Warning Signs Of Stomach Cancer
Early signs of stomach cancer may include:
- Feeling full: Many stomach cancer patients experience a sense of “fullness” in the upper abdomen after eating small meals.
- Heartburn: Indigestion, heartburn or symptoms similar to an ulcer may be signs of a stomach tumor.
- Nausea and vomiting: Some stomach cancer patients have symptoms that include nausea and vomiting. Sometimes, the vomit contains blood.
Other common symptoms of cancers that develop in the stomach may include:
- Unexplained weight loss: Lack of appetite or unexplained weight loss is a common sign of cancer.
- Stomach pain: Abdominal discomfort or pain in the abdomen above the navel may be a symptom of a stomach tumor. Also, swelling or fluid build-up in the abdomen may also be caused by stomach cancer.
Most of the time, stomach cancer isnt the reason for these symptomsthese are common discomforts that may be triggered by conditions such as an ulcer or a stomach virus, or even a heavy meal. Since many early-stage symptoms may easily be ignored or attributed to a more common cause, catching stomach cancer before it advances may be challenging.
Anyone experiencing early-stage stomach cancer symptoms that lack a known cause, or that seem to be worsening is urged to make a doctors appointment. Whether the symptoms are due to stomach cancer or something else, doctors may help identify the problem and treat it properly.
What Are The Main Causes Of Stomach Cancer
There is no single cause of stomach cancer and sometimes it happens without any known risk factors. Lifestyle choices can increase the likelihood of stomach cancer. However, those who experience long-term stomach inflammation from either lifestyle choices or chronic illness are at higher risk.
The common causes of stomach cancer are often related to a medical history that includes:
- H. pylori bacterial infections: A common stomach infection that often causes ulcers.
- Tumors: Other tumors occurring elsewhere in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Stomach polyps: Abnormal tissue growth in the stomach lining.
- Stomach reflex
There are lifestyle changes you can make that may decrease your risk of stomach cancer. These include:
- Having a healthy diet and avoiding
- Processed foods
- Salted foods or increased sodium
Risk factors for stomach cancer that you cannot change, include:
- Your age
- Being male
- Being of Asian, South American or Belarusian descent
- Having a family history of stomach cancer
- Having a history of stomach surgery
- Having pernicious anemia, which is a vitamin deficiency that may be related to either lifestyle or disease
Don’t Miss: What Burns Stomach Fat Fast
Orange And Yellow Shades
Orange poo is often the result of the foods youve eaten but it could also indicate a condition called bile acid malabsorption.
You might also find that your poo floats and can be described as greasy.
Coeliac disease, pancreatic exocrine insufficiency, pancreatitis, type 1 diabetes and type 3c diabetes have all been linked to orange or yellow colour stools.