Q What Are The Symptoms Of Ibs And Ibd
Both are digestive conditions and affect the esophagus, stomach and intestines. IBS is a chronic syndrome made up of a group of symptoms. IBD, on the other hand, refers to inflammation or chronic swelling of the intestines.
IBS symptoms include chronic abdominal pain and changes in bowel habitsdiarrhea and constipation, or alternating between both. Symptoms can vary person to person and can often change over time, making it difficult to manage.
IBS does not develop into IBD or cause permanent harm in your intestines, such as intestinal bleeding, other intestinal diseases or cancer. But it can significantly affect your quality of life. Some have reported they would be willing to give up their essential pleasurescaffeine, use of cell phone and the internet and even sex to be free of IBS symptoms.
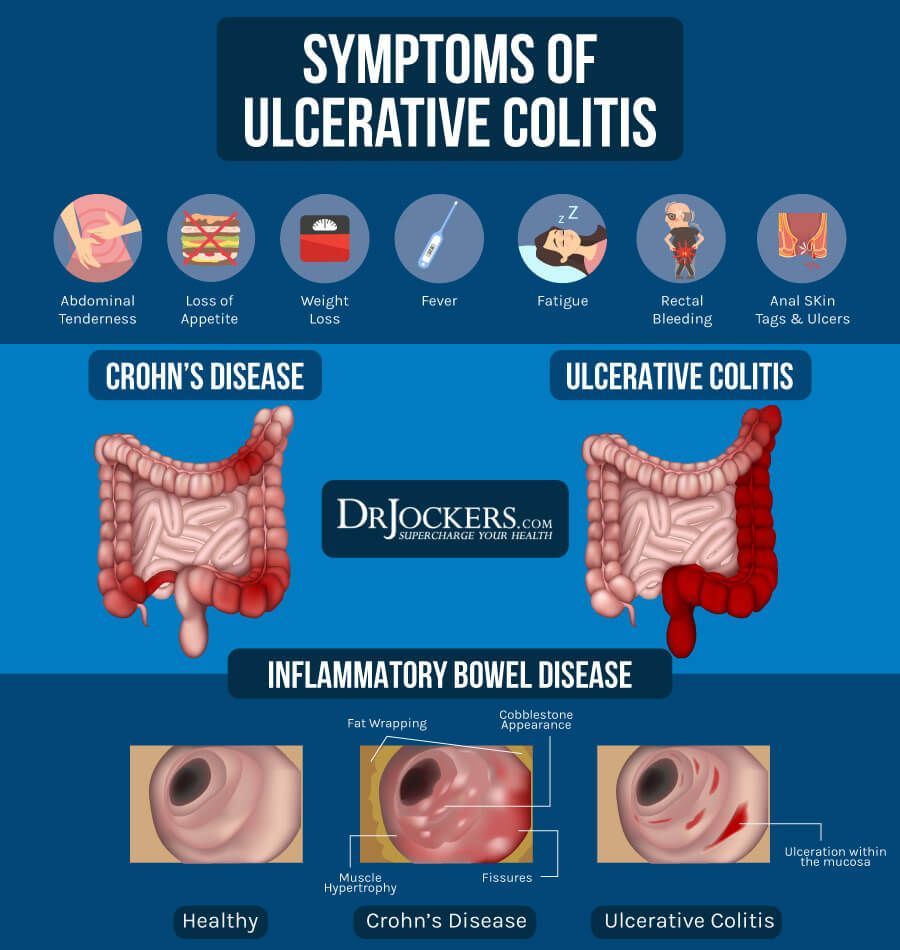
Common forms of IBD include Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis. Both cause chronic inflammation in the GI tract. These conditions can cause rectal bleeding and diarrhea, bloating, abdominal cramping, pain, reduced appetite, unintended weight loss and fatigue.
Also Check: Crohns Disease And Mouth Ulcers
How Does Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Affect My Childs Mental/emotional Health
Like many conditions, ulcerative colitis can have a negative psychological effect, especially on children. They can experience physical, emotional, social and family problems. Because of the medications and/or general stress from the situation, your child may experience:
- Mood swings.
- Worry about appearance and physical stamina.
- Vulnerability because their body doesnt function normally.
- Poor concentration.
- Misunderstandings with friends and family.
Children need mutual support from all family members. Its helpful for the entire family to learn about the disease and try to be empathetic. Seek out a psychiatrist and therapist to help your child manage such challenges of their ulcerative colitis.
Historical Information Important In The Diagnosis Of This Problem
1. When did the pain start or how long have you had the RLQ pain?
Acuity, intensity and duration of pain may be helpful in assessing severity of disease. A sudden onset of pain suggests a serious intra-abdominal event such as an organ perforation or Ischemia or obstruction of a small tubular structure .
A more gradual onset of symptoms suggests an infectious or inflammatory cause , or obstruction of a large tubular structure .
2. Has the pain changed location?
The pain of acute appendicitis may start in the periumbilical area and then a few hours later localize in the RLQ as the peritoneum overlying the inflamed appendix gets affected .
3. Any recent trauma to this area? Any recent abdominal surgery?
Rule out trauma as the cause of pain.
4. Have you ever had this problem before?
A positive response would suggest a chronic intermittent problem e.g. inflammatory bowel disease , diverticulitis, nephrolithiasis.
5. Any history of diverticulitis, Crohns disease or ulcerative colitis, hernias or nephrolithiasis? Any family history of IBD? Any prior abdominal surgeries specifically appendectomy, bowel surgery and in females prior history of salpingo-oopherectomy?
This line of specific questioning helps rule out certain possibilities and make some more likely.
Any intra-abdominal medical devices e.g. ventriculoperitoneal shunts presence raises index of suspicion for intra-abdominal infection .
6. Is the pain dull and constant or is it colicky in nature?
12. Any fever or chills?
Read Also: What Age Can Babies Sleep On Stomach
What Symptoms Do Colitis And Ulcerative Colitis Share
Colitis can cause similar belly and bowel issues no matter the cause. Some symptoms are mild while others are more serious.
General signs of colitis and UC include:
But those arent the only distinctions. Heres a breakdown by colitis type:
Ulcerative colitis . This type of IBD causes sores and constant inflammation in the inner lining of your large intestine. UC often starts in the rectum and extends through the left side of your colon. But some people have colitis throughout most or all of their colon. Thats called extensive colitis or pancolitis.
Crohns colitis. This is a feature of Crohns disease, another type of IBD. Crohns can impact any part of your gastrointestinal tract thats your mouth to your anus. Unlike UC, you may have healthy tissue in between spots of inflammation. Crohns disease can also affect many layers of your GI tract.
Microscopic colitis. This is another type of IBD. Its not related to ulcerative colitis or Crohns disease, but its associated with other autoimmune diseases. Like the name suggests, your doctor has to use a microscope to see any evidence of this kind of colitis.
There are two main forms:
- Collagenous colitis occurs when a protein called collagen builds up in your colon.
- Lymphocytic colitis is when a layer of white blood cells cause colon inflammation.
Some experts think collagenous and lymphocytic colitis may be different phases of the same condition.
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
Lower Left Abdominal Pain

Abdominal pain in the lower left side is more commonly noticed than in the right side. The various organs and structures present in the lower left abdomen include:
- Left ureter
- Left ovary and fallopian tube
- Some part of urinary bladder and the descending bowel .
- Blood vessels, nerves, muscles and skin covering the left abdominal wall.
Any disease or disorder in these structures or organs can generate lower left abdominal pain.
Also Check: How To Prevent Stomach Ulcers
What Role Does Diet And Nutrition Play In Ulcerative Colitis
Diet does not cause the development of ulcerative colitis nor can any special diet cure the disease. However, the foods you or your child eat may play a role in managing symptoms and lengthening the time between flareups.
Some foods may make symptoms worse and should be avoided, especially during flareups. Foods that trigger symptoms are different from person to person. To narrow down what foods affect you, keep track of what you eat each day and how you feel afterward .
Problem foods often include:
- High sugar foods and drinks.
- Carbonated beverages.
- High-fiber foods.
- Alcohol.
In addition to the problem foods listed above, infants, children and teenagers can also experience issues with:
- Salt.
- Dairy products.
Keep a careful eye on your childs diet and nutrition. Their appetite may decrease during a flareup and they might not eat enough to stay healthy, and grow. Also, the inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis may keep their digestive tract from absorbing enough nutrients. This can also affect your childs health. For these reasons, you may have to increase the amount of calories your child consumes.
Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan if you or your child has ulcerative colitis.
Who Gets Ulcerative Colitis And What Causes It
Colitis can develop at any age, but usually first appears in people aged 15 to 30.
Experts are not sure why UC or Crohn’s disease occurs in some people. It may be due to a combination of genetic, environmental and infectious factors that cause a fault in the immune system leading to inflammation of the bowel.
Also Check: Why Is My Lower Stomach Bloated
Continue To Eat And Drink
If your symptoms are severe, you may not feel like eating or drinking. However, this increases the risk of becoming dehydrated. Instead, try to follow a healthy diet, but avoid high-fiber foods for a few weeks. These include bread and cereal made with whole grains, fresh and dried fruit, raw vegetables, seeds and nuts. Eating smaller meals may also help. Also avoid drinking carbonated drinks, which can worsen your symptoms. Instead, drink small amounts of water throughout the day to stay hydrated.
You May Like: List Of Foods Good For Ulcers
Who Is At Risk For Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Most diagnoses of ulcerative colitis are in men between the ages of 15 and 35. The disease course for ASUC can be harder to predict, but it commonly appears between ages 34 and 48.
There is data showing that 54% of those who developed ASUC get it within 1 year of their UC diagnosis 18% developed ASUC within 1 to 5 years of their initial diagnosis and 28% were diagnosed with ASUC more than 5 years after their UC diagnosis.
Additional studies show that those who were diagnosed before the age of 40 had an aggressive disease course, had large or deep ulcers on their colons, higher levels of inflammation, were prescribed steroid medications earlier in their disease, and were at a higher risk of severe disease, including ASUC. Men were at higher risk of needing a colectomy than women.
Recommended Reading: Where Is My Baby At 15 Weeks In My Stomach
Tips On How To Stop A Flare
Learning how to stop, manage, or decrease symptoms during a flare-up can help improve the quality of life of people with UC.
Although managing flare-ups is important, knowing what can trigger a flare-up can help stop one from happening in the first place.
Some of the following strategies may be helpful to implement.
When Should I Take Antispasmodics For Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Some types of antispasmodics are available over-the-counter without a prescription. However, you should always speak to your IBD team before taking one of these medicines, in case it is not suitable for you, or might interact with other medicines you are taking. It is also important to ensure that by taking them you arent masking symptoms that indicate increased disease activity.
If you are prescribed antispasmodics, your IBD team or doctor will tell you how to take the medicine. You can also read the patient information leaflet that comes with them. You may be encouraged to take antispasmodics at specific times of day, in relation to when your symptoms occur.
It is generally recommended that you only take antispasmodics when necessary, stopping if the symptoms settle down.
Read Also: How To Relieve Stomach Cramps
Use A Warm Water Bottle
Heat helps relieve muscle pain, which can be caused by straining your bowels on the toilet, Naik says. To ease cramps, try holding a warm water bottle against your belly just make sure its not hot enough to burn or scald your skin. You can also wrap it in a towel until it cools off.
Practicing yoga can be another way to ease the abdominal pain of ulcerative colitis. A study published in January 2015 in the International Journal of Yoga Therapy found that people with IBD who added one hour of daily yoga to their treatment plan felt less abdominal pain after 8 weeks than people who didnt do yoga.
Another study, published in June 2017 in the journal Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, found that people with ulcerative colitis who did weekly 90-minute sessions of yoga for 12 weeks reported having less disease activity and fewer flare-ups than those who tried other techniques, such as reading self-care books.
What Is The Outlook
Again this depends entirely on the cause of the pain. Some conditions settle very quickly on their own , or with the help of antibiotics . Others can be cured with surgery, such as appendicitis or torsion of the testicle . Some are long-term conditions, for which there is no cure although there are treatments, such those used for people who have Crohns disease. Your doctor should be able to give you an idea of the outlook once a diagnosis has become clear.
Recommended Reading: How To Lose Stomach Fat In 4 Weeks
Also Check: What Is The Best Wet Cat Food For Sensitive Stomach
Does Ibs Get Worse With Age
IBS is long-term disorder of the gut and is an inevitable part of aging. It comes and goes over time. The sensitivity of the gut nerves may elevate with age and the symptoms overlap is possible. Different signs and symptoms related to IBS may show up with age. However, there are some ways like exercise, avoidance of foods that irritate the digestive system etc. that help to help reduce the overall risk of IBS and aid in reducing the symptoms.
You May Like: Sand Beds For Pressure Ulcers
What Is Uc Cramping
Abdominal pain and cramping from UC is most commonly caused by the conditions inflammatory process, according to Christina Ha, MD, a gastroenterologist at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles. Such inflammation usually starts at the rectum and moves throughout the large colon. The greater the inflammation, the more severe the pain.
Don’t Miss: What Does It Mean When You Eat Your Stomach Hurts
What Is The Prognosis For A Person With Colitis
Patients with infectious diarrhea tend to get better relatively quickly with supportive care. Most infections will resolve with or without specific treatment and often do not require antibiotics. Those decisions depend on the patient’s diagnosis.
Patients with inflammatory bowel disease probably will require lifelong treatment to help control their symptoms. The goal, as with any long-term illness, is to allow the patient to live a normal life with minimal symptoms from the disease.
Patients with ischemic colitis need to minimize their risk factors for progressive narrowing of the arteries. These are the same risks as for heart disease and require the same treatment approach, including controlling high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and smoking cessation. Patients with severe ischemia that leads to a dead colon require surgery to remove the gangrenous segment.
How Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Treated
ASUC is a challenging condition to treat. Once you’re admitted to the emergency room, you’ll get a series of tests, including blood tests, stool tests, and an exam of your bowel called a sigmoidoscopy. You’ll also get intravenous fluids to boost hydration.
The average hospital stay for ASUC treatment ranges from 4.6 to 12.5 days. During this time, your health care providers may include a gastroenterologist, colorectal surgeon, dietitian, pharmacist, and stomal therapist. The goal of hospitalizing you is to end the flare, get your symptoms under control, and put the disease into remission. Your doctors will want to make sure that rectal bleeding and diarrhea have stopped and normal bowel movements have returned. Rehospitalization is common.
Intravenous steroid medications are the most common treatment for ASUC. For 30% to 40% of ASUC patients, steroid treatments donât work â and taking steroid medications for more than 10 days increases your risk of complications.
If the steroids donât help within 3 to 5 days, your health care team will start âmedical rescue therapyâ with immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or infliximab.
You might get an operation to remove part of your colon, called a colectomy, if your ASUC doesnât respond to steroids, immunosuppressants, or other medical treatments.
You May Like: How To Lose Stomach Fat Extremely Fast
What Makes It Worse
The reasons why aren’t totally clear. Doctors don’t know why it affects only a small section in one person, but spreads through the entire colon in another. But certain triggers sometimes play a role. These include:
Food. It’s different for everyone, but certain foods can irritate your symptoms. For example:
- Caffeine can make severe diarrhea worse
- Dairy may lead to more diarrhea, gas, and pain
- Fizzy drinks can be a problem if you have gas
- Greasy and fried foods often lead to gas and diarrhea
- High-fiber foods, such as fresh fruits and veggies, whole grains, corn, nuts, and seeds, can be hard on you
- Spicy foods can be tough to handle
Stress. It can trigger flare-ups and make your symptoms much harder to deal with. It’s especially challenging because just having ulcerative colitis can bring on more of it.
Skipping meds. Even when you’re in remission, it’s very important to take your meds. In the best case, they prevent flare-ups. And even if not, they can help keep things under control.
Follow these 5 tips to help control your ulcerative colitis flare-ups.
Is It Important To Treat A Flare Early Or Is It Ok To Wait A Bit
Inflammation typically does not resolve without treatment and early intervention has a better outcome than waiting to treat. At an early stage of a flare, a more optimal baseline treatment is often enough to get the inflammation under control. If you wait, there is a greater risk that you might need drugs with greater side effects, such as oral steroids. By waiting, you will have to manage longer with your symptoms before getting relief. Living with constant or longer periods of inflammation might increase your risk for future complications, as inflammation might cause damage to the gut wall that accumulates in severity with each flare.
If you are experiencing worsening symptoms, you have probably already had the flare for some time without symptoms. Evidence shows that a stool test for inflammation in the colon, called fecal calprotectin, is often elevated for two to three months before any symptoms appear. Your colon might also start to show visual evidence of inflammation before you have symptoms, or at least indicate an increased risk for a flare.
Also Check: How To Tighten Stomach Muscles
Psychological Therapies In Uc
In addition to antidepressants, psychological therapies have also been shown to be beneficial in IBS. These include cognitive behavioral therapy and gut-directed hypnotherapy, and both are recommended by national guidelines for the management of IBS., However, evidence for their use as an effective treatment for UC, particularly in those with IBS-type symptoms, is lacking. A Cochrane review investigated the efficacy of psychotherapy, patient education, and relaxation techniques for IBD. Outcomes assessed included health-related quality of life, coping, emotional status, and disease activity. In total, 21 studies were included, but there was no clear benefit identified for any of the psychological interventions in adults with UC for any of the outcomes of interest.
Another systematic review of 16 studies of psychological interventions, including stress management, psychodynamically informed therapy, CBT, and hypnosis assessed their effects on anxiety and depression, quality of life, and IBD activity. CBT and psychodynamically informed therapy were beneficial for anxiety and depression, but they appeared to have no effect on disease activity, whereas hypnotherapy, used in two studies, demonstrated a beneficial effect on disease activity, but not anxiety, depression, or quality of life.